Understanding the Australian Boiler and Pressure Vessel Grades and Terminology

XLERPLATE® steel's boiler and pressure vessel range are plate products specially designed using a fully killed, fine grained carbon-manganese steel. These products are manufactured to the Australian Boiler and Pressure Vessel Standard, AS 1548:2008, the standard has a number of options in terms of available grades and the supply conditions for those grades. This document sets out to explain the grade designations and supply conditions that are available under the standard and considerations associated with each of the available supply conditions.
Grade Designation
All grades in the Australian Boiler and Pressure Vessel Standard AS 1548:2008 have grade names in the following form:
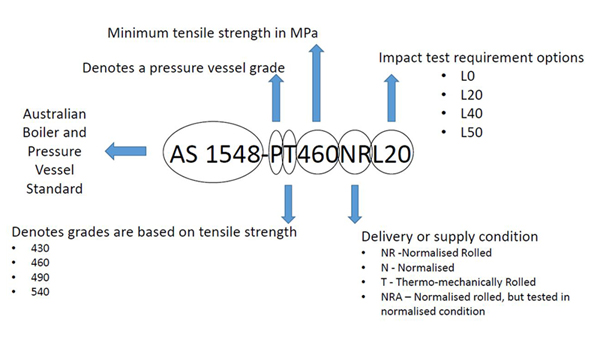
Supply Conditions
There are four supply conditions available consisting of Normalised Rolling (NR), Normalised (N), NRA Designated Grades (NRA) and Thermo-mechanical Controlled Rolling (T). These supply conditions are explained further below.
Normalised Rolling (NR)
A rolling process in which the final deformation (rolling pass) is carried out in a certain temperature range that produces a material condition equivalent to that obtained after normalising.
Normalised (N)
The heat treatment process undertaken after rolling where the XLERPLATE® steel is heated between 870 – 930°C. Normalised grades may be replaced by Normalised Rolled grades with agreement between the purchaser and the manufacturer.
NRA Designated Grades (NRA)
Grades with an NRA supply condition are supplied with the plate rolled in a Normalised Rolled condition, but with tests carried out on normalised and stress relived test samples. The fabricator MUST normalise or hot form grades with an NRA designation to ensure that the steel meets the required properties. Failure to carry out normalising or hot forming of the steel supplied may mean the XLERPLATE® fails to meet the requirements of the Standard.
Thermo-mechanical Controlled Rolling (T)
A rolling process in which a significant amount of deformation (rolling) takes place at temperatures below the normalising range, leading to a fine grained structure. TMCR is used to achieve improve strength and toughness with relatively low CEQ chemistries. TMCR is not suitable for hot forming at temperatures >620°C as this may adversely affect the properties of T grade steels. The T grades are not generally suitable for hot forming.
Considerations Associated with the Supply Condition Options
| Supply Condition | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Normalised Rolled (NR) |
|
|
| Normalised (N) |
|
|
| NRA Designated (NRA) |
|
|
| Thermo-mechanical Controlled Rolled (T) |
|
|